It may support diabetes care as an adjunct. Calibrated foot pressure can modulate autonomic balance, reduce sympathetic drive, and enhance vagal tone, potentially easing stress-related glycaemic variability. Mechanoreceptor stimulation may improve peripheral perfusion and microcirculation, with possible benefits for neuropathic discomfort. It does not replace medication, monitoring, or wound care. Contraindications include active foot ulcers, infection, or severe ischemia. Pre/post-session glucose checks are advised. Qualified therapists individualize pressure and techniques to vascular and sensory status. Further details outline safety, mechanisms, and session expectations.
Understanding It and How It Works

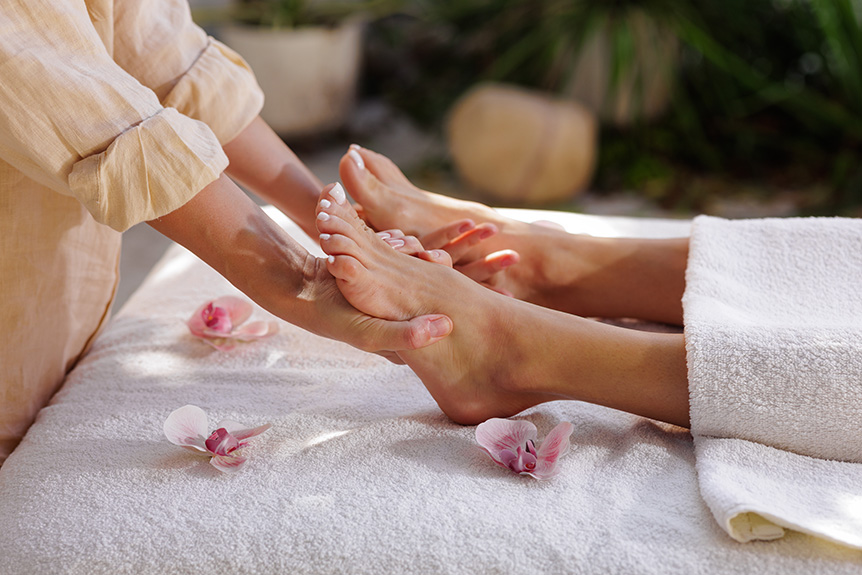
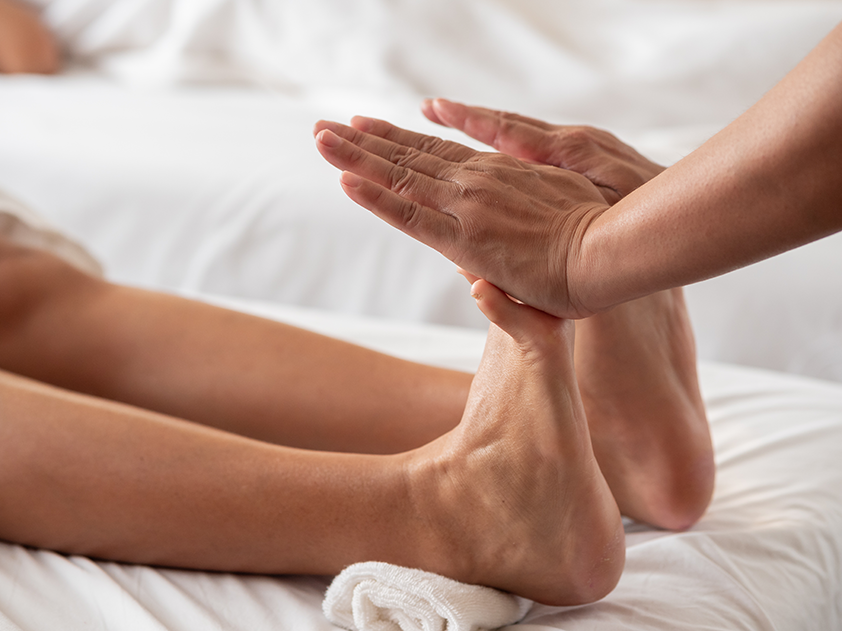
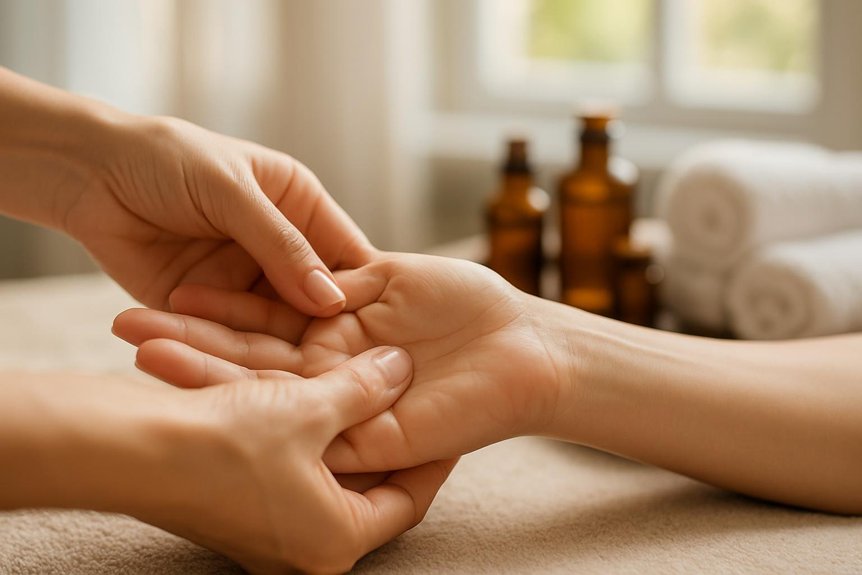
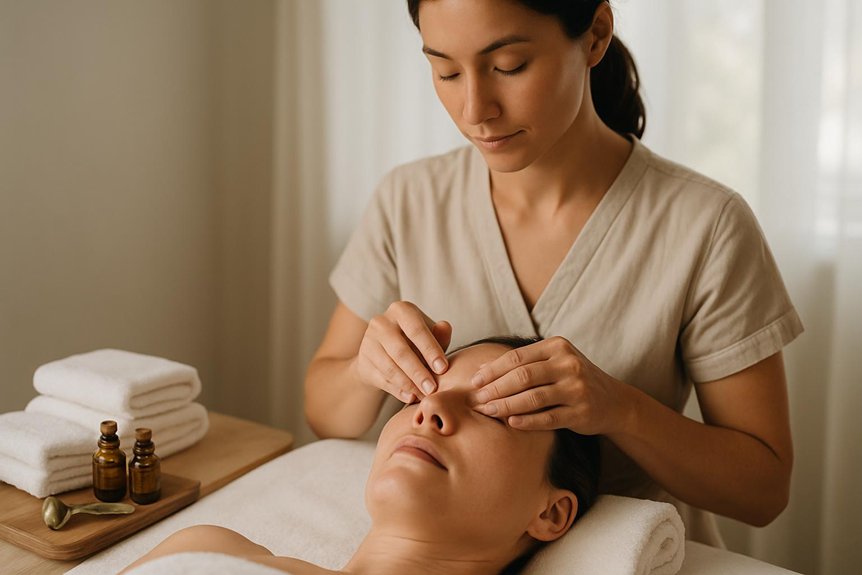
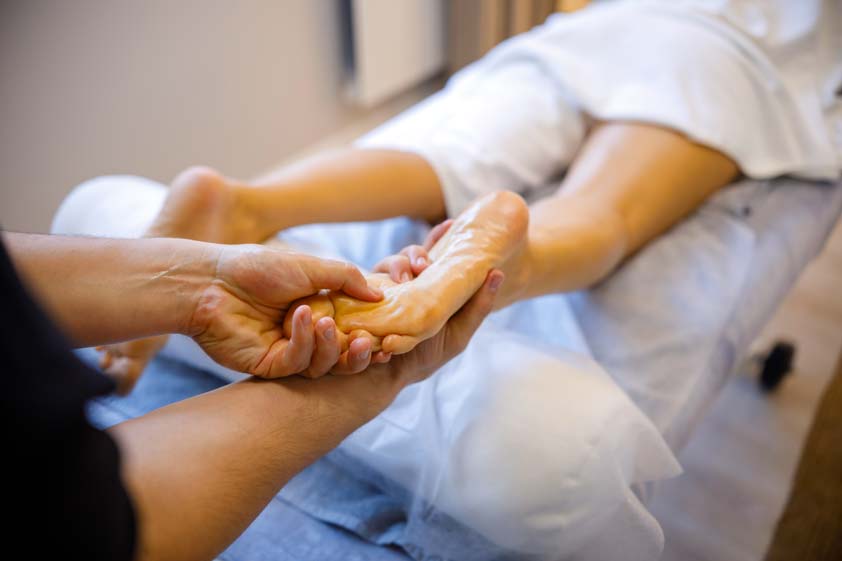
It is a manual therapy that applies calibrated pressure to specific points on the feet, hands, or ears that correspond to musculoskeletal regions, organ systems, and autonomic pathways.
The working model integrates cutaneous mechanoreceptor stimulation, segmental spinal modulation, and autonomic balance.
Pressure on reflex points activates A-beta afferents, dampening nociceptive traffic via gate-control mechanisms and influencing viscerosomatic reflex arcs.
Evidence suggests downstream effects on heart rate variability, peripheral circulation, and muscle tone, consistent with parasympathetic upregulation and reduced sympathetic drive.
At Spa & Massage in London, therapists map reflex zones with anatomical precision, adjust pressure by tissue response, and monitor real-time changes in skin temperature and tone.
Sessions are structured, not symbolic: measured holds, graded compressions, and rhythmic sequences that prioritise safety, clear endpoints, and reproducible outcomes.
Many clients seek out the healing power of zone therapy for its potential to promote balance in organ systems and support overall wellbeing.
The Connection Between Zone Therapy and Blood Sugar Regulation
Building on the neurophysiological mechanisms outlined above, the question for glycaemic control is whether targeted foot reflex stimulation can modulate autonomic tone, microcirculation, and stress reactivity in ways that influence glucose dynamics.
Emerging data suggest three plausible pathways. First, reflex input may rebalance sympathetic–parasympathetic activity, potentially improving hepatic glucose output and peripheral uptake.
Second, improved distal perfusion could aid skeletal muscle glucose disposal by enhancing capillary recruitment.
Third, downregulation of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal stress signalling may lower counter-regulatory hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
From Spa & Massage’s clinical perspective, it is framed as an adjunct to medical care, not a substitute. Therapists prioritise precise, tolerable pressure, paced breathing, and warm compresses to reinforce vagal tone.
Blood glucose monitoring remains essential; any zone therapy plan is coordinated with existing medical advice and medications.
Potential Benefits for People Living With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
For individuals with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, reflexology may support peripheral circulation and modulate nociceptive signaling, offering adjunctive relief for neuropathic discomfort.
By promoting parasympathetic activity and reducing perceived stress, it may indirectly influence glucose variability via effects on cortisol and autonomic balance.
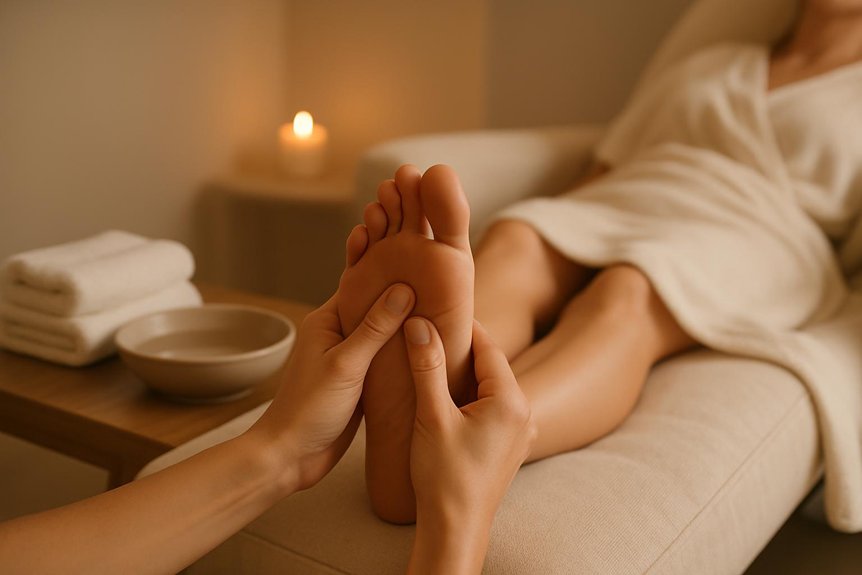
At Spa & Massage, therapists apply structured foot and lower-leg techniques with light-to-moderate pressure to target these mechanisms while advising clients to maintain standard diabetes care and glucose monitoring.
Circulation and Neuropathy Relief
How might targeted foot stimulation influence peripheral circulation and nerve discomfort in diabetes?
Evidence suggests this may enhance microvascular flow via local vasodilation, shear-stress–mediated nitric oxide release, and improved calf-muscle pump activity. Gentle, rhythmic pressure can modulate sympathetic tone, reducing peripheral vasoconstriction that commonly limits blood supply in neuropathic feet.
For neuropathy, mechanoreceptor input from the plantar surface may downregulate pain signaling through gate-control mechanisms and support neuroplasticity. Light-to-moderate pressure avoids nociceptor irritation while promoting tissue perfusion.
At Spa & Massage clinics in London, therapists use cautious, graded techniques—avoiding areas with ulcers, severe oedema, or acute inflammation—and adapt session length for sensory sensitivity. Clients are guided on post-session foot checks, hydration, and elevation.
It is positioned as supportive care, complementing medical management and podiatry.
Stress Reduction and Glucose
Why does stress management matter for glycaemic control in diabetes?
Acute and chronic stress activate sympathetic outflow and the HPA axis, elevating cortisol, adrenaline, and glucagon. These hormones drive hepatic gluconeogenesis, transient insulin resistance, and higher fasting and post‑prandial glucose. Sleep disruption and pain amplify the effect.
For many, reducing autonomic arousal improves time‑in‑range.
Evidence suggests relaxation therapies can modestly lower perceived stress and heart rate, with downstream glycaemic benefits.
Zone therapy, delivered calmly and consistently, may enhance parasympathetic tone via vagal pathways and pressure‑mediated analgesia, supporting steadier glucose patterns alongside medication, diet, and activity.
At Spa & Massage clinics in London, therapists tailor this to promote deep relaxation, emphasising slow diaphragmatic breathing and gentle foot work.
Clients are advised to monitor glucose closely post‑session and hydrate, then integrate regular sessions within broader self‑management.
Managing Diabetic Neuropathy and Foot Discomfort With Reflex Point Treatment

When peripheral nerves are damaged by chronic hyperglycaemia, altered microvascular perfusion and nerve inflammation drive the pain, numbness, and dysesthesia typical of diabetic neuropathy—particularly in the feet. It does not reverse neuropathy, but targeted pressure to plantar reflex zones may modulate nociceptive signaling, enhance cutaneous blood flow, and reduce sympathetic overactivity, easing discomfort.
Small trials suggest improvements in pain scores, thermal thresholds, and sleep quality.
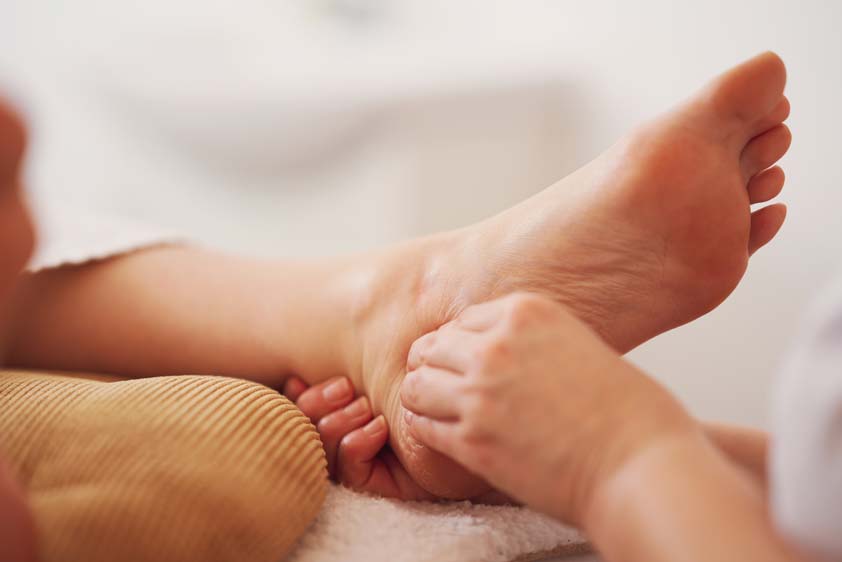
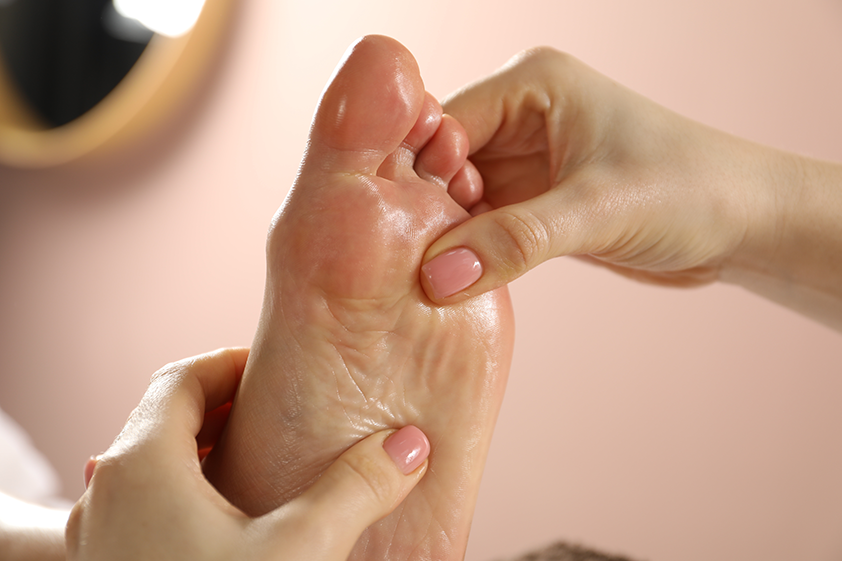
At Spa & Massage clinics in London, therapists apply gentle, graded pressure along the great toe (medial plantar hallux), metatarsal heads, and calcaneal regions, progressing only within client tolerance. Neutral, hypoallergenic oils reduce friction without excessive glide, preserving precise contact.
Sessions emphasise warm-up, slow pacing, and post-session foot checks. Clients are encouraged to report sensation changes, cramping, or delayed soreness to refine subsequent treatments.
Safety Considerations and When to Avoid This Therapy
Prudently applied, it is generally low risk for people with diabetes, but specific contraindications and precautions warrant attention. Poorly perfused feet, active ulcers, cellulitis, or unhealed wounds are clear reasons to avoid foot pressure therapy; tissue stress may impair healing and spread infection.
Severe peripheral neuropathy reduces protective sensation, so pressure should be minimal and well monitored. Anticoagulation, advanced peripheral arterial disease, and edema also warrant modified or deferred work to prevent bruising or ischemic compromise. Recent thrombosis, fever, or acute illness are exclusions.
Glycaemic variability matters: firm foot work can transiently influence autonomic tone; clients should arrive fed, carry glucose, and monitor levels.
At Spa & Massage, therapists screen for red flags, coordinate with medical guidance, and adapt techniques to skin integrity, sensation, and circulation.
What to Expect in a Massage Session at Spa & Massage
At Spa & Massage, a massage session for someone with diabetes begins with a focused consultation to document medical history, glycaemic control, neuropathy status, skin integrity, and circulation concerns.
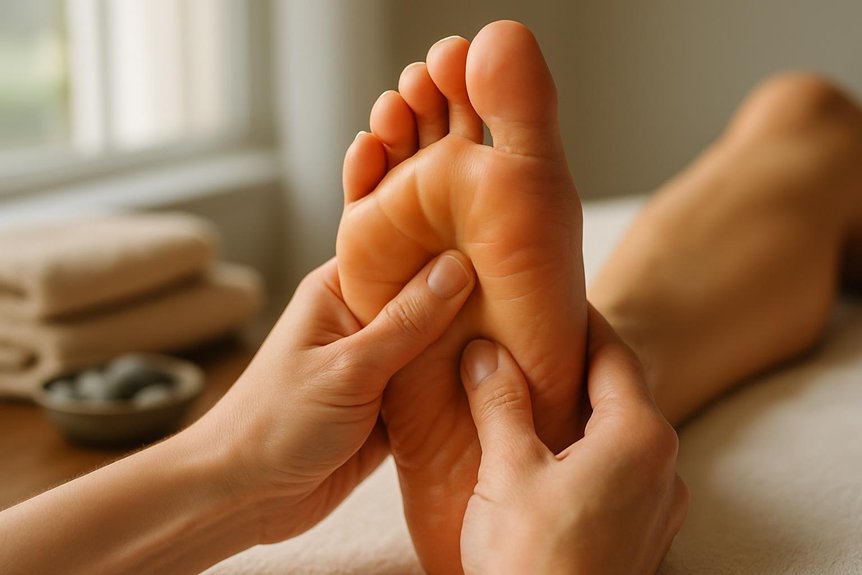
Therapists then apply graded thumb-walking and pressure techniques to mapped foot reflex zones, modulating intensity to protect insensate areas and avoid compromised tissue while aiming to influence autonomic balance and microcirculatory dynamics.
Aftercare includes hydration, gentle foot checks, glucose monitoring as indicated, and guidance on signs requiring medical review, consistent with our clinics’ safety protocol.
Consultation and Assessment
How does a massage session begin at Spa & Massage? It starts with a focused consultation. Therapists record medical history, diabetes type, medications (including anticoagulants), neuropathy symptoms, wound status, and glycaemic control patterns. They ask about hypoglycaemia risk, peripheral vascular disease, and skin integrity.
Objective assessment includes visual foot inspection, capillary refill, edema check, temperature asymmetry, and monofilament or light-touch screening to gauge protective sensation.
They map concerns to reflex zones, prioritising areas relevant to autonomic balance, stress modulation, and circulation. Session goals are defined: relaxation to reduce sympathetic drive, gentle inputs to support microvascular comfort, and strict protection of vulnerable tissues.
In our London clinics, therapists document baseline pain, sleep quality, and fatigue scores to enable outcome tracking. Consent covers pressure limits, positioning, and glucose safety planning.
Techniques and Aftercare
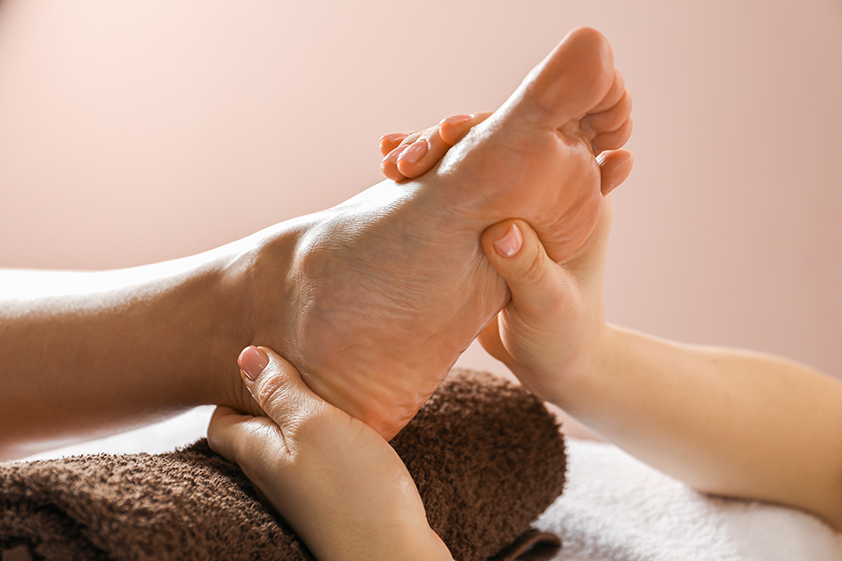
A session proceeds with precise, low-to-moderate pressure thumb walking and static holds across mapped foot reflex zones, adjusted for diabetes-related neuropathy and vascular status. Therapists at Spa & Massage modulate force to avoid provoking ischemic discomfort, focusing on zones associated with autonomic balance, microcirculation, and stress modulation.
Warm compresses may precede work to enhance tissue perfusion; lubricant is minimal to maintain grip and control.
Aftercare emphasizes gentle foot checks, hydration, and paced rewarming to support vasodilation. Clients are advised to monitor glucose as relaxation can transiently alter sympathetic tone and perceived energy intake.
Our therapists recommend elevating feet briefly post-session, wearing breathable socks, and avoiding vigorous heat on insensate areas. Any redness, numbness change, or delayed soreness warrants feedback before the next appointment.
How Often to Book and How to Complement Medical Care

Initial scheduling typically follows a weekly massage session for 4–6 weeks to assess response. Then shifts to biweekly or monthly maintenance if outcomes are stable (e.g., reduced stress, improved sleep, perceived neuropathic discomfort relief). Frequency is adjusted to glycaemic variability, neuropathic symptoms, and recovery capacity.
In Spa & Massage clinics, therapists document session goals, pressure tolerance, and autonomic cues (skin temperature, foot perfusion, breathing rate) to guide pacing.
It should complement, not replace, diabetes care. Clients are advised to continue medications, glucose monitoring, dietary plans, and physical activity, and to share its schedules with their GP or diabetes team.
Mechanistically, sessions may downshift sympathetic arousal and support sleep quality, indirectly aiding self-management adherence.
Therapists at Spa & Massage coordinate timing around meals and insulin to reduce hypoglycaemia risk and observe red flags requiring medical review.
Self-Care Tips and Foot Health Between Sessions
Between this massage sessions, diligent foot care and self-regulation strategies help protect tissue integrity and support autonomic balance. Daily inspection under good light detects blisters, fissures, or colour change early—critical when neuropathy dulls warning signals. Gentle washing, careful drying between toes, and emollient application to plantar skin preserve barrier function and reduce shear.
In our London clinics, therapists recommend fragrance-free urea- or ceramide-based creams and avoiding oils between toes to limit maceration.
Regular, low-impact walking enhances peripheral perfusion; paired with diaphragmatic breathing and slow exhales, it downshifts sympathetic tone. Properly fitted shoes and seamless socks reduce pressure points; nail edges are trimmed straight to prevent ingrowth. Hydration and stable glucose targets support microvascular health.
Any non-healing lesion, numbness progression, or acute swelling warrants prompt medical review.
Choosing Qualified Therapists and Tailoring Your Treatment
Consistent self-care gains are best sustained when matched with skilled reflex point treatment delivered by therapists trained to work with diabetes. Competent practitioners screen for neuropathy, peripheral arterial disease, glycaemic variability, and skin integrity, then adapt pressure, pacing, and zone selection to protect sensation and circulation.
Evidence suggests that it may modulate autonomic tone, reduce stress reactivity, and support microvascular perfusion—mechanisms relevant to glucose regulation and foot health.
At Spa & Massage, therapists document medications, HbA1c history, footwear issues, and wound risk, then agree goals: stress downshifting, sleep quality, or specific foot comfort. They use lighter, sustained contacts over risk areas, avoid callus disruption, and schedule reviews aligned to glycaemic patterns.
Clients receive aftercare on daily foot checks, moisturising, and load management. Clear outcomes tracking guides progression or referral.
Conclusion
In summary, it does not treat diabetes, yet it may serve as a steady rudder—supporting relaxation, sleep, and comfort while clients pursue evidence-based care. By modulating stress responses and encouraging local circulation, sessions can complement medication, nutrition, and activity. With screening for neuropathy, vascular issues, and skin integrity, risks remain low. At Spa & Massage, structured protocols, hygiene, and individual tailoring underpin practice. For most, integrating zone therapy thoughtfully may enhance wellbeing without straying from established clinical guidelines.